Introduction
An accounts receivable dashboard can efficiently visualize, monitor, and analyze accounts receivable functions. This aspect of the receivables dashboard provides the current state of the company’s receivables, including essential detailed measures such as KPI, additional summary information, notifications, and trends. Connected to the organization’s ERP or billing systems, it retrieves timely updated financial and operational data in A/R, providing complete information on all activities.
Explore key AR Dashboard metrics to optimize financial tracking and improve decision-making in our comprehensive guide.
If the ratio is higher, the implication is that A/R is being converted to cash in less frequent periods. Consequently, the more frequently A/R is collected, the more cash flow and liquidity the business organization enhances.
Understanding accounts receivable dashboards.
What is an account reversible dashboard?
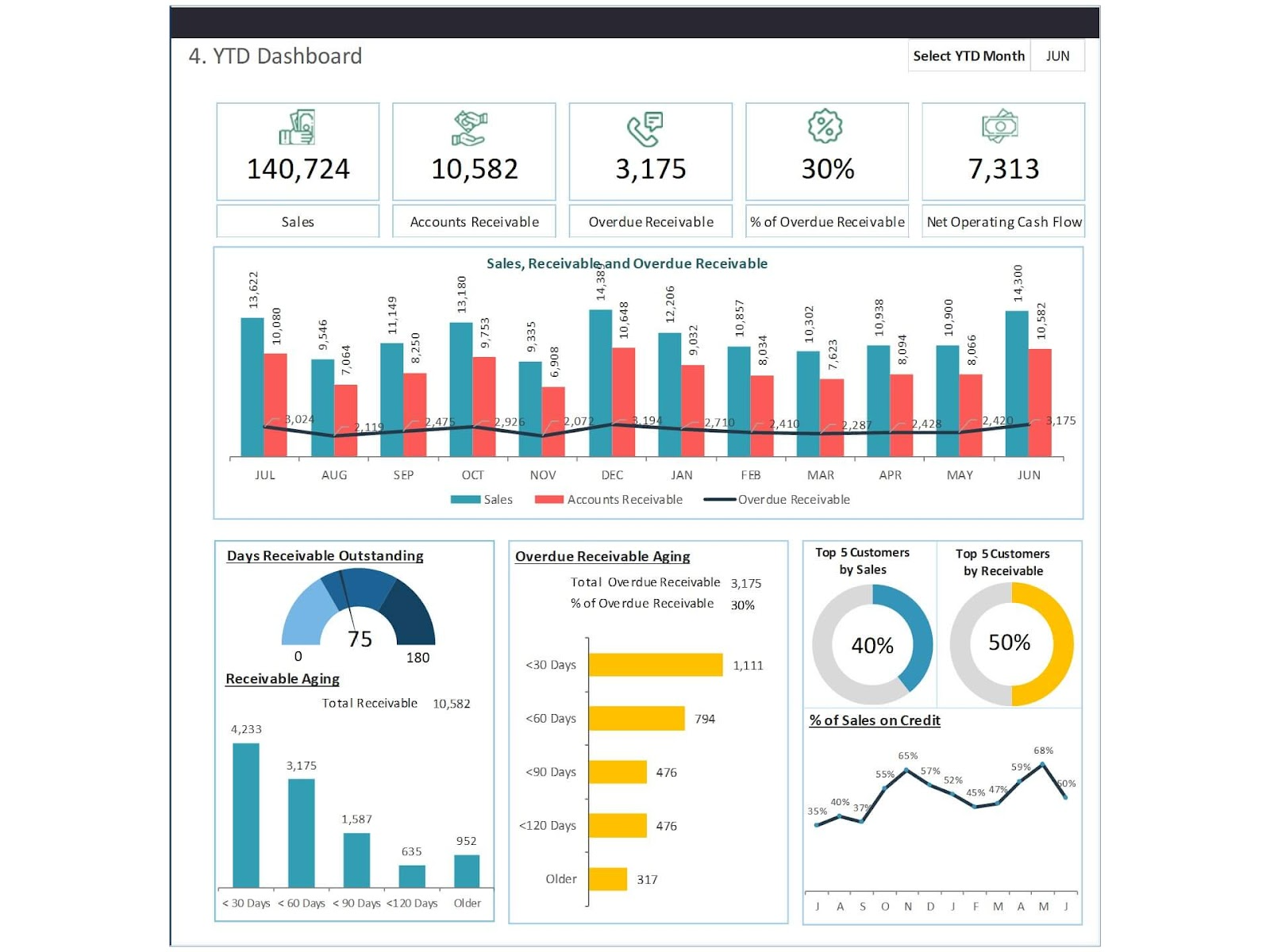
Business accounting processes are frequently contrasted with a cockpit’s gauges and warning lights. They help to give actual-time information regarding the condition of the receivables within the company and can indicate issues. An account reversible dashboard is a picture of convenient, easily understood data that displays KPIs, critically summarized data, and measures related to the accounts currently owned and processed by the AR teams. The simplified real-time financial and operational data are extracted from the organizations’ ERP system and can be filtered according to the employee type.
The accounts reversible dashboard’s constituents include details of a company’s receivables, AR turnover, days sales outstanding and aging reports, and master customer files. The dashboard also measures an AR department’s performance through KPIs such as processing output, the department’s capacity to recover amounts due, and the error rate.
Key features of an effective AR dashboard
- Real-time updates
Nothing beats real-time data, as it is always up to date. Real-time data is beneficial from a strategic point of view because it allows teams to be much more reactive as soon as issues surface.
- Customizable interface
A dashboard has to grow into an application that meets all your BI requirements. It may not be possible with Off-The-Shelf applications; at least from time to time, there can be corruption of essential data. This is why companies hire custom dashboard development companies like ours, I.e., Biz Infograph.
Essential metrics for your AR dashboard
Days Sales Outstanding (DSO)
DSO is the average period it takes to collect cash for accounts receivables. It assists in establishing overseas collection efficiency and a general cash flow position. Usually, a lower DSO figure is favorable, but sometimes, it could be partially true because it depends on the business cyclicality.
This is done by dividing the average accounts receivable by the total credit sales and multiplying by the number of days in the period to get DSO.
Aging accounts receivable
Aging Accounts Receivable is a measure featured on your accounts reversible dashboard template involving data collection from clients segmented into different data classes. Aging reports group receivables by the number of days since the invoice was issued.
Techniques to address the problem of aging receivables include:
- Contacting the customers frequently.
- Giving rebates for early payments.
- Putting more rigid credit lines in place for the clients.
Current vs overdue receivables
Based on the analysis, the current AR dashboard should consist of the Current vs. Overdue Receivables, where you compare the timely payments made to invoices and overdue invoices. This differentiation is essential for evaluating the company’s cash flow and determining major liquidity problems. Identifying the aged outstanding receivables assists in formulating early measures to reduce bad debts and achieve good financial health.
Percentage of receivables beyond terms
The factors that should be included in the AR dashboard are, among others, the Percentage of Receivables Beyond Terms; this shows how many invoices remain unpaid beyond the agreed terms. It reflects customers’ payment behavior and may indicate conditions hindering cash flow. It refers to enhancing compliance and ensuring that all terms are well understood, proposed payments are to be made within the shortest time possible, and where there is a problem, it is resolved within the shortest time possible.
Accounts Receivable Turnover Ratio
AR turnover ratio measures how often AR is collected and replenished. Generally, a high turnover is desirable, though in this case, it contributes to the company’s downfall and can be considered undesirable.
For instance, a turnover ratio of 12, standard in the retail trade, indicates that AR is collected and replaced 12 times a year.
The accounts receivable turnover ratio in AR is given by Total Credit Sales divided by Average Accounts Receivable.
Leveraging AR Dashboard for Strategic Decisions
Identifying trends and patterns
The use of an AR dashboard enriches the company’s decision-making processes. In other words, by emphasizing the analysis of patterns and tendencies, companies can use historical data with relatively high predictability for tendencies. For example, understanding when apparel shoppers make their purchases frequently depending on the year will help avoid stocking up on a particular stock at the wrong time. Likewise, doing a similar analysis of customer behavior trends would help businesses manage their marketing practices better and thus increase customer loyalty.
When forming these scenarios, information is utilized in such a manner as to allow for decision-making that would lead to better performance and superior competitive positioning.
Risk management and mitigation
The AR dashboard makes risk management faster as the accounts with high-risk values can be quickly detected. This guarantees efficiency in identifying risks, which include any irregularities in the transactional pattern or conspicuous variations in financial processes. These risks can be prevented effectively with the help of other activities, such as automated alerts and patient-specific risk management techniques.
For instance, they mark shady transactions for further investigation or apply higher authentication methods to avoid fraudulent purchases. Being proactive helps prevent such risks, thereby protecting the company’s financial and image assets and enhancing corporate risk management and business resilience.
Best practices for AR dashboard management
Regular updates and reviews
Thus, regularly updating and reviewing the AR dashboard’s best practices is essential. Timely updates enable decision-making, improving the relevance of the decisions made. A necessary aspect of this process is to set up meetings that take place regularly, and this ensures that the changes are made incrementally and also align with organizational goals and plans. It instills flexibility whereby tactics can be changed soon, following emerging market patterns and trends.
Integrating with other financial systems
Implementing AR dashboards in conjunction with ERP and CRM has several advantages. It allows for efficient data transfer and helps show deeper details of the organization’s financial performance and customers. Thus, integration makes workflow more active and improves the quality of decision-making. Therefore, integrating data from diverse sources helps organizations effectively plan resource usage and efficiency gains at the organizational level.
Conclusion
Using an AR dashboard is beneficial for improving critical financial decisions as it gives valuable information. Anales such as revenue increase, profitability ratios, and cash flow trends balance provide a total picture of the company’s finances. These measures assist in discovering where changes need to be made, how resources should be utilized optimally, and where potential risks can be best managed.
Thus, the adoption of AR dashboards provides an opportunity for businesses to improve the level of transparency, flexibility, and strategic management. This makes stakeholders better placed to make good decisions based on their information and be able to offer flexible solutions when there is a change in the market. By adopting this technology, organizations promote a culture of innovation and competition, which is helpful in today’s environment characterized by rapid changes and advancement of various industries.